Pulse Profiles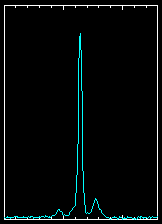
|  ".AU" File ".AU" File
 ".WAV" File ".WAV" File
| PSR B0329+54
This pulsar is a typical, normal pulsar, rotating with a period of
0.714519 seconds, i.e. close to 1.40 rotations/sec.
|
|
 ".AU" File ".AU" File
 ".WAV" File ".WAV" File
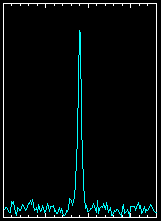
| PSR B0833-45, The Vela Pulsar
This pulsar lies near the centre of the Vela supernova remnant, which
is the debris of the explosion of a massive star about 10,000 years
ago. The pulsar is the collapsed core of this star, rotating with a
period of 89 milliseconds or about 11 times a second.
|
|
 ".AU" File ".AU" File
 ".WAV" File ".WAV" File
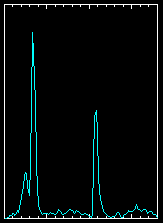
| PSR B0531+21, The Crab Pulsar
This is the youngest known pulsar and lies at the centre of the Crab
Nebula, the supernova remnant of its birth explosion, which was
witnessed by Europeans and Chinese in the year 1054 A.D. as a day-time
light in the sky. The pulsar rotates about 30 times a second.
|
|
 ".AU" File ".AU" File
 ".WAV" File ".WAV" File
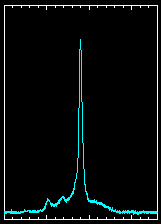
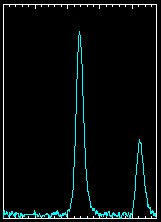
| PSR J0437-4715
This is a recently discovered millisecond pulsar, an old pulsar which
has been spun up by the accretion of material from a binary companion
star as it expands in its red giant phase. The accretion process
results in orbital angular momentum of the companion star being
converted to rotational angular momentum of the neutron star, which is
now rotating about 174 times a second.
|
|
 ".AU" File ".AU" File
 ".WAV" File ".WAV" File
| PSR B1937+21
This is the fastest known pulsar, rotating with a period of
0.00155780644887275 seconds, or about 642 times a second. The surface
of this star is moving at about 1/7 of the velocity of light and
illustrates the enormous gravitational forces which prevent it flying
apart due to the immense centrifugal forces.
|