 |
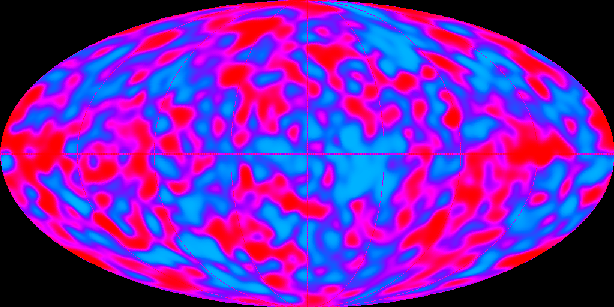
| The COBE Satellite measured the 3K microwave background radiation. Astronomers were able to produce a map of the distribution of the radiation throughout the Universe. The clumpiness of the radiation meant that galaxies could form. Photo: NASA |
Everything in the universe exerts a gravitational pull on everything else, and this slows down the universal expansion. The ultimate fate of the universe depends on the amount of mass contained within it, that is, the mean density of the universe. There is a critical density, which if reached will be sufficient to just stop the expansion of the universe. This is similar to a ball thrown in the air; the Earth's gravity eventually stops the ball, and it begins to fall back. There is considerable uncertainty in our knowledge of the amount of matter in the universe. However, two possibile outcomes exist.
Whatever the ultimate fate of the universe, it is clear that the universe does not allow for the possibility of eternal life.
Currently the most popular theory of the origin of the Universe is the so called "Big Bang" theory. According to this theory, the Universe originated from an extremely hot, dense fireball (of matter and radiation) which exploded, sending matter outwards. As it expanded, it cooled sufficiently for matter to form into galaxies. The presently observed expansion of the universe (as evidenced by the recession of the galaxies) is considered to be due to this initial explosion. The big bang occurred some 10 to 20 thousand million years ago, and over this time the universe has evolved to its present state.
The Universe will expand forever: If the mean density is less than the critical density, then there is insufficient mass within the universe to stop the expansion - the universe will expand forever. Ultimately, the galaxies will move increasingly further apart. Star formation within the galaxies will eventually cease as the star forming material is exhausted. The universe will slowly cool to absolute zero: a heat death will occur. Life will be unable to exist.
The Universe will collapse in on itself: If the mean density exceeds the critical density, then the expansion of the universe will eventually cease, and the universe will begin to contract. Eventually, a fireball like that which initiated the universe's expansion will result. This is referred to as the "Big Crunch". If this were to happen, it is estimated that it is some 50 thousand million years in the future (at least ten times the remaining life of the Sun). It may be that the universe expands and contracts in a cyclic way and may, indeed, have been doing so in the past - this is the so-called "Oscillating Theory of the Universe".